Emotions are an inherent and intricate part of the human experience. They color our
perceptions, guide our behaviors, and shape our interactions with the world. Emotion
regulation, the process of managing and modulating one’s emotional responses, is a critical skill
that plays a pivotal role in our mental and emotional well-being. Many of our students start
with working on identifying the emotion to determine how best to deal with it. While we may
always have a stigma towards mental health in our society, this perspective is shifting and
therefore, many of us adults are just now learning about our emotions and how to regulate
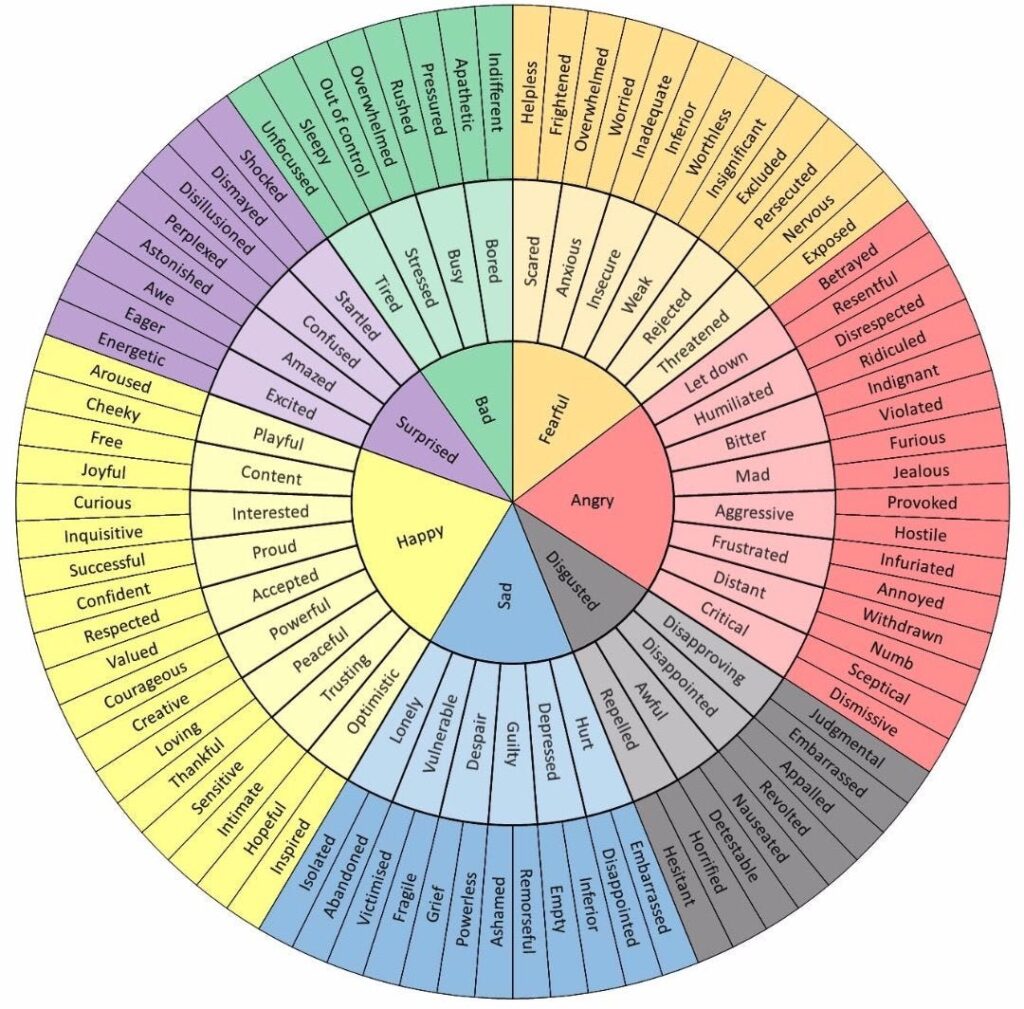
them. Oftentimes, we use the phrase “I feel” to describe a non-emotion without even realizing
it (e.g., “I feel like you were rude to me” [this is an evaluation, not an emotion]; “I feel that isn’t
the right thing to do” [also not an emotion]). Take a minute to check in with yourself and
reference the emotion wheel below to complete the sentence, “I feel _”.
The Significance of Emotion Regulation
Emotion regulation is a multifaceted skill that allows individuals to navigate the ever-
changing landscape of their feelings. It involves the ability to recognize, understand, and
effectively manage emotions to achieve desired outcomes. This skill is vital for several reasons:
- Mental Health: Emotion regulation is closely linked to mental health. Poor regulation
can lead to a range of emotional disorders, including anxiety, depression, and borderline
personality disorder. Conversely, effective regulation can enhance psychological well-
being and resilience. - Interpersonal Relationships: Our ability to regulate emotions significantly influences our
interactions with others. Effective regulation fosters empathy, communication, and
conflict resolution, making it easier to build and maintain healthy relationships. - Decision-Making: Emotions often play a central role in decision-making. Effective
regulation allows individuals to make rational choices by preventing impulsive,
emotionally driven actions that may lead to regret. - Physical Health: Emotions can impact physical health through their effects on stress and
immune function. Poor emotion regulation can contribute to chronic stress, which is
associated with a host of health problems.
Emotion Regulation Strategies
Emotion regulation encompasses a variety of strategies, each tailored to different
emotional experiences and contexts. This is why emotion identification is an important place to
start, as certain emotions and situations require different strategies than others. It is all also
person-dependent because what works for you or for me may not work for our student/child.
Some common strategies that we use at Lake House include:
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Mindfulness practices encourage individuals to observe
their thoughts and feelings without judgment. This awareness helps individuals become
more attuned to their emotions and better equipped to manage them. Mindfulness-
based interventions have been shown to reduce stress and improve emotional
regulation. I lead a weekly “Mindful Movement” group where we explore different
mindfulness exercises and movement activities (e.g., yoga) to ground ourselves in our
bodies. To be in a room full of quiet adolescents that are meditating and practicing
breath awareness and body scanning is often the highlight of my week. JAMA Psychiatry
published a randomized clinical trial that compared the effectiveness of mindfulness-
based stress reduction (MBSR) to an antidepressant and found that mindfulness
meditation is as effective at treating anxiety as the antidepressant Lexapro. 1 Exercise has
also been shown to have a positive impact on mood and emotional regulation. Engaging
in regular physical activity can reduce stress, release endorphins, and improve overall
emotional well-being. - Currently, we are using Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) skills training across our
milieu. This means the students and the staff are getting weekly lessons that align to
prompt more frequent use in the milieu. DBT teaches us to embrace the duality of the
human experience through mindfulness, distress tolerance, interpersonal effectiveness,
“walking the middle path”, and emotion regulation, so this provides an umbrella
framework to cover multiple strategies. DBT is an evidence-based practice and highly
reputable in the field for effectiveness with decreasing self-harm, anger, and inpatient
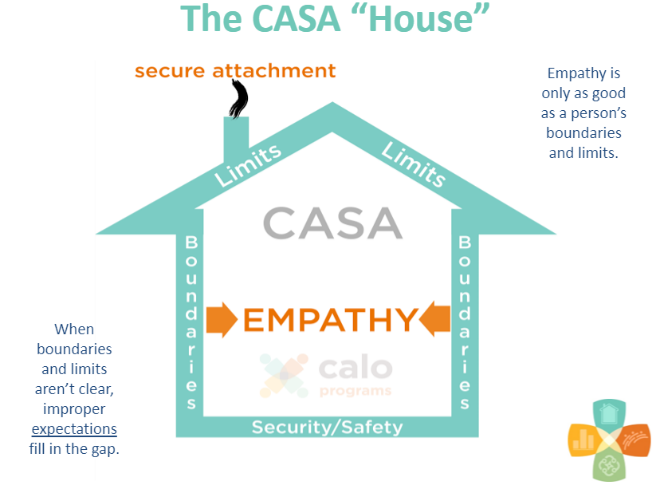
hospitalization days. - By now, you know that Lake House uses the CASA framework. CASA stands for
commitment, acceptance, security, and attunement. We use this as markers for
student’s progress, the focus for our family workbook resource, and the theme for our
family workshops. Combined, these four focus areas lead a family to co-regulate and for
the student to self-regulate.
Conclusion
Emotion regulation is a fundamental skill that underpins our mental, emotional, and
social well-being. Its significance lies not only in its individual benefits but also in its potential to
create healthier, more harmonious family systems and societies. As we continue to explore the
intricacies of our emotions and refine our regulation strategies, we move closer to a world
where empathy, resilience, and understanding are the guiding principles of our interactions. By
embracing emotion regulation, we are getting closer to Embark’s “Big Hairy Audacious Goal” of
taking adolescent and young adult anxiety, depression, and suicide rates from the all-time highs
of today to all-time lows by 2028.
[1] Hoge EA, Bui E, Mete M, Dutton MA, Baker AW, Simon NM. Mindfulness-based stress
reduction vs escitalopram for the treatment of adults with anxiety disorders: a randomized clinical
trial. JAMA Psychiatry. Published online November 9, 2022. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2022.3679